8. What Is the Cost Per Equivalent Unit for Materials? (Round Your Answer to 2 Decimal Places.)
Procedure Costing
29 Explicate and Compute Equivalent Units and Full Cost of Production in an Initial Processing Stage
As described previously, process costing can take more than one work in procedure account. Determining the value of the piece of work in procedure inventory accounts is challenging because each product is at varying stages of completion and the computation needs to exist washed for each department. Trying to make up one's mind the value of those partial stages of completion requires application of the equivalent unit computation. The equivalent unit computation determines the number of units if each is manufactured in its entirety before manufacturing the next unit of measurement. For example, forty units that are 25% complete would exist ten (40 × 25%) units that are totally complete.
Direct material is added in stages, such as the outset, centre, or end of the process, while conversion costs are expensed evenly over the process. Often in that location is a dissimilar percentage of completion for materials than there is for labor. For instance, if fabric is added at the outset of the process, the xl units that are 100% complete with respect to material and 25% complete with respect to conversion costs would exist the same every bit twoscore units of cloth and ten units (40 × 25%) completed with conversion costs.
For example, during the month of July, Rock City Percussion purchased raw material inventory of $25,000 for the shaping department. Although each section tracks the direct material information technology uses in its own department, all material is held in the material storeroom. The inventory volition be requisitioned for each department as needed.
During the calendar month, Rock City Percussion's shaping section requested $10,179 in direct material and started into production 8,700 hickory drumsticks of size 5A. There was no outset inventory in the shaping section, and 7,500 drumsticks were completed in that department and transferred to the finishing department. Wood is the simply direct textile in the shaping department, and it is added at the beginning of the procedure, so the piece of work in process (WIP) is considered to exist 100% consummate with respect to straight materials. At the end of the month, the drumsticks still in the shaping department were estimated to be 35% complete with respect to conversion costs. All materials are added at the beginning of the shaping process. While beginning the size 5A drumsticks, the shaping section incurred these costs in July:

These costs are then used to calculate the equivalent units and total production costs in a four-pace process.
Footstep One: Determining the Units to Which Costs Will Be Assigned
In add-on to the equivalent units, it is necessary to rails the units completed too every bit the units remaining in ending inventory. A similar process is used to business relationship for the costs completed and transferred. Reconciling the number of units and the costs is office of the process costing system. The reconciliation involves the total of beginning inventory and units started into production. This total is called "units to account for," while the total of beginning inventory costs and costs added to production is called "costs to be accounted for." Knowing the total units or costs to account for is helpful since it too equals the units or costs transferred out plus the amount remaining in catastrophe inventory.
When the new batch of hickory sticks was started on July 1, Rock City Percussion did not have whatever first inventory and started 8,700 units, so the total number of units to account for in the reconciliation is 8,700:

The shaping section completed vii,500 units and transferred them to the testing and sorting department. No units were lost to spoilage, which consists of any units that are not fit for auction due to breakage or other imperfections. Since the maximum number of units that could maybe exist completed is 8,700, the number of units in the shaping department'due south ending inventory must be one,200. The total of the 7,500 units completed and transferred out and the 1,200 units in ending inventory equal the 8,700 possible units in the shaping department.

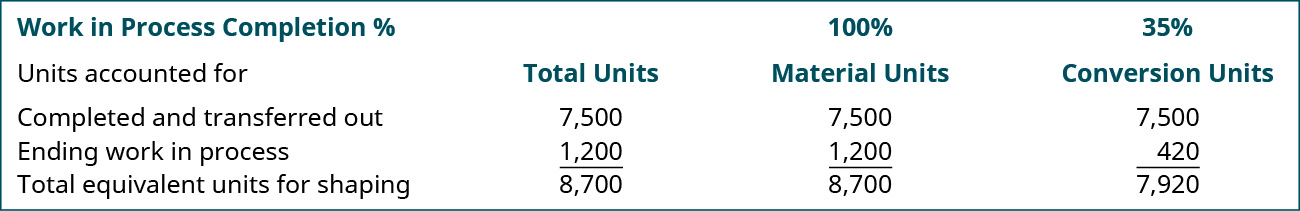
Footstep Two: Computing the Equivalent Units of Product
All of the materials have been added to the shaping department, just all of the conversion elements have not; the numbers of equivalent units for material costs and for conversion costs remaining in ending inventory are unlike. All of the units transferred to the next department must be 100% consummate with regard to that department'due south cost or they would non be transferred. And then the number of units transferred is the same for material units and for conversion units. The process cost system must calculate the equivalent units of production for units completed (with respect to materials and conversion) and for ending work in process with respect to materials and conversion.
For the shaping department, the materials are 100% consummate with regard to materials costs and 35% consummate with regard to conversion costs. The 7,500 units completed and transferred out to the finishing section must be 100% consummate with regard to materials and conversion, and so they brand upwardly 7,500 (7,500 × 100%) units. The 1,200 ending piece of work in process units are 100% consummate with regard to material and have 1,200 (1,200 × 100%) equivalent units for fabric. The 1,200 catastrophe work in process units are just 35% complete with regard to conversion costs and correspond 420 (1,200 × 35%) equivalent units.
Step Three: Determining the Cost per Equivalent Unit
Once the equivalent units for materials and conversion are known, the cost per equivalent unit is computed in a similar way every bit the units deemed for. The costs for material and conversion need to reconcile with the total beginning inventory and the costs incurred for the section during that month.
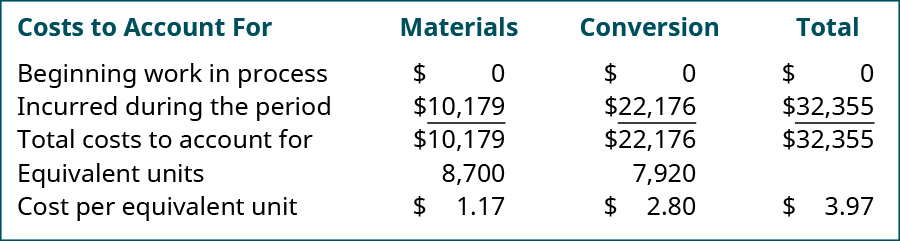
The total materials costs for the period (including whatsoever beginning inventory costs) is computed and divided by the equivalent units for materials. The same process is then completed for the full conversion costs. The total of the cost per unit for material ($1.17) and for conversion costs ($2.80) is the full price of each unit transferred to the finishing department ($3.97).
Step Four: Allocating the Costs to the Units Transferred Out and Partially Completed in the Shaping Section
Now you lot can determine the cost of the units transferred out and the cost of the units notwithstanding in procedure in the shaping department. To calculate the appurtenances transferred out, simply accept the units transferred out times the sum of the 2 equivalent unit costs (materials and conversion) because all items transferred to the next department are complete with respect to materials and conversion, so each unit brings all its costs. But the ending WIP value is adamant by taking the product of the piece of work in process material units and the price per equivalent unit for materials plus the product of the work in process conversion units and the cost per equivalent unit of measurement for conversion.
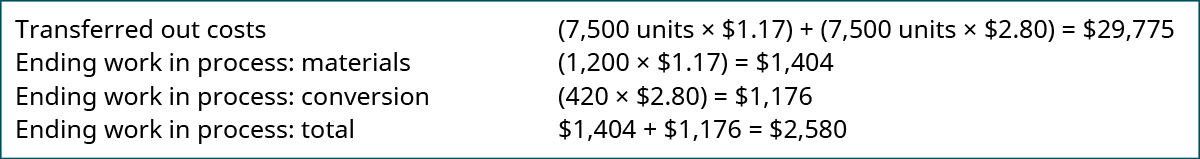
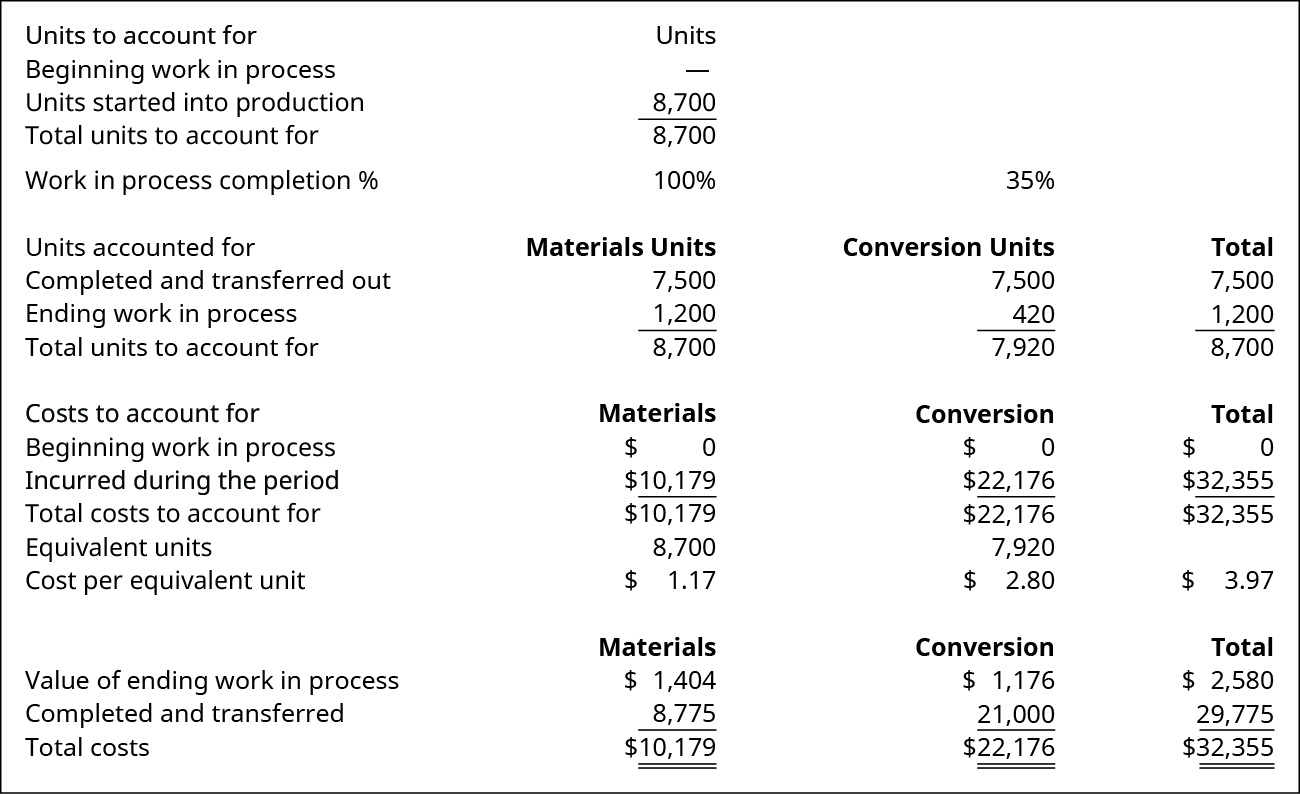
This data is accumulated in a production cost report. This report shows the costs used in the grooming of a product, including the cost per unit for materials and conversion costs, and the corporeality of piece of work in process and finished goods inventory. A complete production cost study for the shaping department is illustrated in (Figure).
Product Cost Study for the Shaping Department. (attribution: Copyright Rice Academy, OpenStax, under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license)
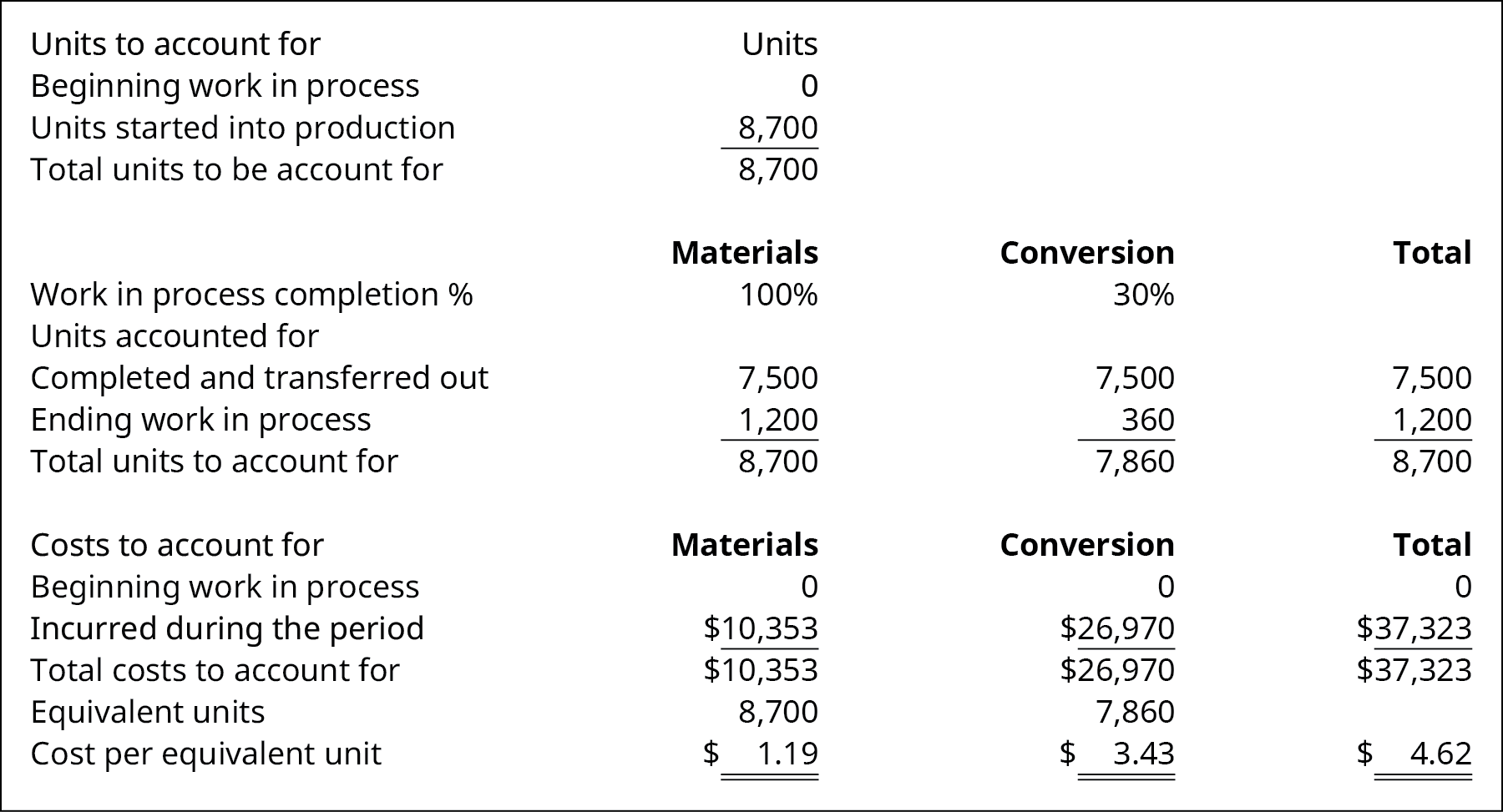
Calculating Inventory Transferred and Work in Process Costs
Kyler Industries started a new batch of paint on October 1. The new batch consists of 8,700 cans of paint, of which seven,500 was completed and transferred to finished goods. During October, the manufacturing process recorded the following expenses: straight materials of $10,353; direct labor of $17,970; and applied overhead of $9,000. The inventory all the same in process is 100% complete with respect to materials and 30% complete with respect to conversion. What is the toll of inventory transferred out and work in process? Assume that there is no beginning work in process inventory.
Solution
Cardinal Concepts and Summary
- Process costing has a work in process inventory account for each department.
- Equivalent units of production for materials may differ from the equivalent units for conversion costs.
- The total units to account for is the number of units in the beginning work in procedure inventory plus the number of units started into production; this total likewise represents the sum of the number of units completed and the number of units in the ending work in process inventory.
- The cost per equivalent unit of measurement for materials is the total of the material costs for the beginning piece of work in process inventory and the total of cloth costs incurred during the period.
- The cost per equivalent unit for conversion costs is the full of the conversion costs for the beginning work in process inventory and the total of conversion costs incurred during the period.
- The cost of units transferred to the adjacent department is the number of units transferred times the total of the toll per equivalent unit of material plus the price per equivalent unit for conversion costs.
(Figure)Direct material costs $3 per unit, direct labor costs $v per unit of measurement, and overhead is practical at the charge per unit of 100% of the straight labor price. What is the value of the inventory transferred to the next section if get-go inventory was two,000 units; ix,000 units were started; and 1,000 units were in ending inventory?
- $1,000
- $xiii,000
- $130,000
- $20,000
(Figure)Beginning inventory and direct material toll added during the month total $55,000. What is the value of the ending work in process inventory if beginning inventory was ii,000 units; nine,000 units were started; and 1,000 units were in catastrophe inventory?
- $ane,000
- $5,000
- $50,000
- $55,000
(Figure)The initial processing department had a commencement inventory of 750 units and an ending inventory of 1,350 units, and information technology started 9,500 units into production. How many were transferred out to the adjacent section?
- 750
- 1,350
- 8,900
- 10,250
(Figure)There were 1,000 units in ending inventory subsequently transferring xvi,000 units to finished goods inventory. If the showtime inventory was two,000 units, how many units were started in process?
- 1,000
- 2,000
- 15,000
- 17,000
(Figure)What are the iv steps involved in determining the toll of inventory transferred from one department to the adjacent and the toll of work in process inventory?
Stride 1: Determine the units to which costs are assigned. Step 2: Compute the equivalent units of production. Stride 3: Determine the toll per equivalent unit. Step 4: Allocate the costs to the units transferred out and the units partially completed.
(Effigy)What is the weighted-boilerplate method for computing the equivalent units of product?
(Effigy)Given the following data, determine the equivalent units of ending work in process for materials and conversion nether the weighted-boilerplate method:
- starting time inventory of 2,500 units is 100% complete with regard to materials and sixty% complete with regard to conversion
- 18,000 units were started during the menstruation
- 17,500 units were completed and transferred
- ending inventory is 100% consummate with materials and 65% complete with conversion
(Figure)In that location were 1,700 units in beginning inventory that were 40% consummate with regard to conversion. During the month, 8,550 units were started and 9,000 were transferred to finished goods. The catastrophe work in process was 60% complete with regard to conversion costs, and materials are added at the beginning of the procedure. What is the full amount of equivalent units for materials and conversion at the end of the month using the weighted-average method?
(Figure)A company has 1,500 units in ending work in procedure that are 30% complete after transferring out 10,000 units. All materials are added at the showtime of the process. If the cost per unit is $four for materials and $7 for conversion, what is the cost of units transferred out and in ending work in process inventory using the weighted-average method?
(Figure)There were 2,400 units in ending work in process inventory that were 100% complete with regard to textile and 25% complete with regard to conversion costs. Ending piece of work in process inventory had a toll of $9,000 and a per-unit of measurement fabric cost of $two. What was the conversion cost per unit using the weighted-average method?
(Figure)How many units must be in ending inventory if beginning inventory was 15,000 units, 55,000 units were started, and 57,000 units were completed and transferred out?
(Figure)How many units must have been completed and transferred if beginning inventory was 75,000 units, ending inventory was 72,000 units, and 290,000 units were started?
(Effigy)Using the weighted-boilerplate method, compute the equivalent units of production if the kickoff inventory consisted of 20,000 units; 55,000 units were started in product; and 57,000 units were completed and transferred to finished goods inventory. For this process, materials are added at the beginning of the procedure, and the units are 35% complete with respect to conversion.
(Figure)Using the weighted-average method, compute the equivalent units of product for a new visitor that started 85,000 units into production and transferred 67,000 to the second section. Assume that starting time inventory was 0. Conversion is considered to occur evenly throughout the process, while materials are added at the beginning of the process. The ending inventory for Equivalent Units: Conversion is 9,000 units.
(Figure)Mazomanie Farm completed 20,000 units during the quarter and has 2,500 units still in process. The units are 100% complete with regard to materials and 55% complete with regard to conversion costs. What are the equivalent units for materials and conversion?
(Effigy)What are the total costs to account for if a company's first inventory had $231,432 in materials, $186,450 in conversion costs, and added direct material costs ($4,231,392), straight labor ($2,313,392), and manufacturing overhead ($ane,156,696)?
(Figure)A company started the calendar month with 8,329 units in piece of work in process inventory. It started 23,142 units and had an catastrophe inventory of 9,321. The units were 100% complete to materials and 67% complete with conversion. How many units were transferred out during the flow?
(Effigy)Given the following information, make up one's mind the equivalent units of catastrophe work in process for materials and conversion using the weighted-average method:
- Kickoff inventory of 750 units is 100% complete with regard to materials and xxx% complete with regard to conversion.
- ix,500 units were started during the flow.
- 8,900 units were completed and transferred.
- Catastrophe inventory is 100% complete with regard to materials and 68% complete with regard to conversion.
(Effigy)There were 2,000 units in beginning inventory that were lxx% consummate with regard to conversion. During the month, xv,000 units were started, and 16,000 were transferred to finished goods. The catastrophe work in procedure was 55% complete with regard to conversion costs, and materials are added at the get-go of the process. What is the total amount of equivalent units for materials and conversion at the cease of the month using the weighted-average method?
(Figure)A visitor has 100 units in catastrophe work in process that are 40% complete after transferring out 750 units. If the toll per unit is $5 for materials and $2.50 for conversion, what is the cost of units transferred out and in ending piece of work in process inventory using the weighted-average method?
(Figure)In that location were 1,500 units in ending piece of work in process inventory that were 100% complete with regard to material and 60% consummate with regard to conversion costs. Ending piece of work in procedure inventory had a cost of $7,200 and a per-unit material cost of $iii. What was the conversion cost per unit of measurement using the weighted-average method?
(Figure)Using the weighted-average method, compute the equivalent units of production if the beginning inventory consisted of 20,000 units, 55,000 units were started in product, and 57,000 units were completed and transferred to finished goods inventory. For this process, materials are lxx% consummate and the units are 30% consummate with respect to conversion.
(Figure)What are the total costs to account for if a visitor's beginning inventory had $23,432 in materials and $eighteen,450 in conversion costs, and added direct material costs ($41,392), direct labor ($23,192), and manufacturing overhead ($62,500)?
(Figure)A company started the month with 4,519 units in work in process inventory. Information technology started 15,295 units and had an catastrophe inventory of 4,936. The units were 100% complete to materials and 30% consummate with conversion. How many units were transferred out during the period?
(Figure)Pant Risers manufactures bands for self-dressing assistive devices for mobility-dumb individuals. Manufacturing is a one-footstep process where the bands are cut and sewn. This is the information related to this yr's product:
Catastrophe inventory was 100% complete every bit to materials and seventy% complete as to conversion, and the total materials cost is $57,540 and the full conversion price is $36,036. Using the weighted-boilerplate method, what are the unit costs if the visitor transferred out 17,000 units? What is the value of the inventory transferred out and the value of the ending WIP inventory?
(Figure)During March, the following costs were charged to the manufacturing department: $xiv,886 for materials; $xiv,656 for labor; and $13,820 for manufacturing overhead. The records prove that 30,680 units were completed and transferred, while 2,400 remained in ending inventory. There were 33,080 equivalent units of cloth and 31,640 of conversion costs. Using the weighted-average method, what is the cost of inventory transferred and the residual in work in process inventory?
(Figure)Materials are added at the first of a production process, and catastrophe piece of work in process inventory is thirty% complete with respect to conversion costs. Utilize the information provided to consummate a production price report using the weighted-average method.
(Figure)Narwhal Swimwear has a beginning work in process inventory of 13,500 units and transferred in 130,000 units earlier ending the month with 14,000 units that were 100% complete with regard to materials and xxx% complete with regard to conversion costs. The toll per unit of material is $v.fourscore and the cost per unit for conversion is $8.20 per unit. Using the weighted-average method, what is the amount of material and conversion costs assigned to the department for the month?
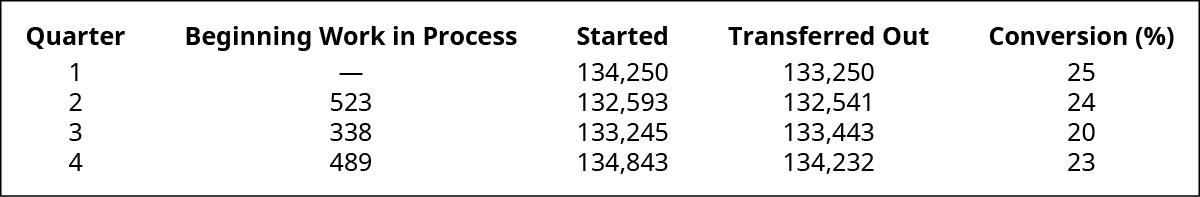
(Figure)The post-obit data show the units in beginning work in process inventory, the number of units started, the number of units transferred, and the percent completion of the ending work in process for conversion. Given that materials are added at the first of the procedure, what are the equivalent units for textile and conversion costs for each quarter using the weighted-boilerplate method? Assume that the quarters are independent.
(Figure)The following product costs are available for Stellis Company on the product of erasers: direct materials, $22,000; straight labor, $35,000; manufacturing overhead, $17,500; selling expenses, $17,600; and administrative expenses; $13,400.
- What are the prime costs?
- What are the conversion costs?
- What is the total product cost?
- What is the total period cost?
- If 13,750 equivalent units are produced, what is the equivalent material cost per unit of measurement?
- If 17,500 equivalent units are produced, what is the equivalent conversion cost per unit of measurement?
(Figure)The post-obit product costs are available for Kellee Company on the product of eyeglass frames: straight materials, $32,125; direct labor, $23.l; manufacturing overhead, applied at 225% of direct labor cost; selling expenses, $22,225; and administrative expenses, $31,125. The directly labor hours worked for the month are 3,200 hours.
- What are the prime number costs?
- What are the conversion costs?
- What is the full product cost?
- What is the total menses price?
- If vi,425 equivalent units are produced, what is the equivalent textile cost per unit?
- What is the equivalent conversion toll per unit of measurement?
(Effigy)Vexar manufactures nails. Manufacturing is a one-step procedure where the nails are forged. This is the information related to this year's production:
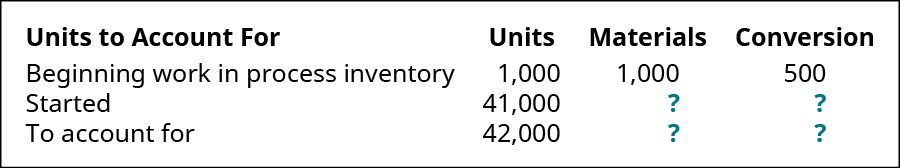
Ending inventory was 100% complete as to materials and 70% complete as to conversion, and the total materials cost is $115,080 and the total conversion cost is $72,072. Using the weighted-average method, what are the unit costs if the visitor transferred out 34,000 units? Using the weighted-average method, prepare the company'southward process cost summary for the month.
(Figure)During March, the following costs were charged to the manufacturing department: $22,500 for materials; $45,625 for labor; and $l,000 for manufacturing overhead. The records show that 40,000 units were completed and transferred, while 10,000 remained in ending inventory. There were 45,000 equivalent units of material and 42,500 units of conversion costs. Using the weighted-boilerplate method, ready the visitor's process cost summary for the month.
(Figure)Ardt-Barger has a beginning work in process inventory of 5,500 units and transferred in 25,000 units earlier ending the month with 3,000 units that were 100% complete with regard to materials and eighty% consummate with regard to conversion costs. The cost per unit of textile is $5.45, and the price per unit of measurement for conversion is $half-dozen.20 per unit. Using the weighted-boilerplate method, set the company's process price summary for the month.
(Effigy)The following data testify the units in beginning work in process inventory, the number of units started, the number of units transferred, and the percent completion of the ending work in process for conversion. Given that materials are added at the beginning of the procedure, what are the equivalent units for material and conversion costs for each quarter using the weighted-average method? Assume that the quarters are independent.
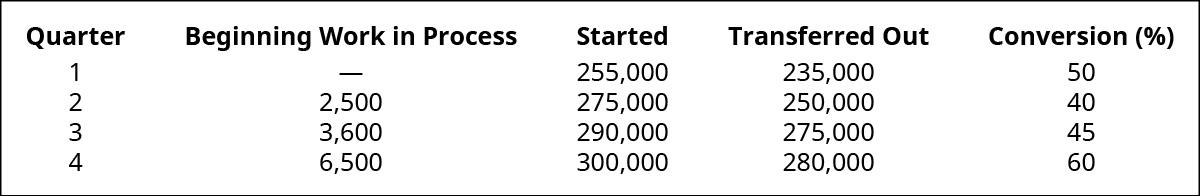
(Effigy)The post-obit data show the units in beginning work in procedure inventory, the number of units started, the number of units transferred, and the pct completion of the ending work in process for conversion. Given that materials are added 50% at the beginning of the procedure and fifty% at the end of the process, what are the equivalent units for material and conversion costs for each quarter using the weighted-average method? Assume that the quarters are independent.

(Figure)The post-obit data bear witness the units in start work in process inventory, the number of units started, the number of units transferred, and the percent completion of the catastrophe work in process for conversion. Given that materials are added fifty% at the commencement of the process and 50% at the finish of the procedure, what are the equivalent units for fabric and conversion costs for each quarter using the weighted-average method? Presume that the quarters are independent.

Glossary
- production cost report
- shows the costs used in the preparation of a product, including the toll per unit for materials and conversion costs and the amount of work in procedure and finished goods inventory
- spoilage
- any units that are not fit for sale due to breakage or other imperfections
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/principlesofaccountingv2openstax/chapter/explain-and-compute-equivalent-units-and-total-cost-of-production-in-an-initial-processing-stage-2/
0 Response to "8. What Is the Cost Per Equivalent Unit for Materials? (Round Your Answer to 2 Decimal Places.)"
Post a Comment